In the fast-evolving landscape of electronics manufacturing, PCB printing plays a crucial role. A recent industry report indicates that PCB production is expected to grow significantly, reaching $75 billion by 2026. This surge is driven by the increasing demand for consumer electronics, automotive technologies, and IoT devices. Notably, PCB printing is at the forefront of this transformation.
PCB printing not only improves the efficiency of production but also enhances the quality of electronic devices. Advanced techniques enable manufacturers to create more complex designs without sacrificing reliability. For instance, high-density interconnect (HDI) technology revolutionizes how components are integrated. Yet, challenges remain. Many manufacturers struggle with quality control and production errors that can lead to costly recalls.
While the future of PCB printing looks promising, organizations must continually adapt. Staying updated with technological advancements is crucial. The importance of robust processes and quality assurance cannot be overlooked. Addressing these challenges will ensure that PCB printing remains essential to modern electronics.
PCB printing plays a crucial role in the realm of modern electronics manufacturing. Circuit boards are the backbone of electronic devices. According to a report by IPC, the global PCB market reached $70 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow at a rate of 5.4% annually. This growth reflects the increasing demand for more advanced electronics.
The efficiency of PCB printing directly influences production speed. Traditional methods can be slow and labor-intensive. In contrast, modern PCB printing methods, such as additive manufacturing, streamline this process. This technology reduces waste and shortens lead times. However, challenges remain. Ensuring high reliability and quality in printed circuits is essential. Failure rates due to manufacturing defects can undermine product trust.
Moreover, there is a shift towards miniaturization. Smaller gadgets need more compact PCBs with finer traces. Reports indicate that microvia technology is becoming vital in achieving this. While microvias can enhance performance, they also increase complexity. Manufacturers must navigate these challenges to stay competitive. The balance between innovation and reliability is delicate, and progress in PCB printing must be continually assessed.
| Dimension | Description | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Different substrates such as FR-4, CEM-1, and flexible materials | Selection impacts durability and performance characteristics |
| Layer Count | Number of conductive layers in a circuit board | Affects complexity and functionality of the PCB |
| Printed Circuit Design | Routing of tracks and placement of components | Critical for ensuring electrical connections are correctly made |
| Manufacturing Process | Includes etching, drilling, and solder mask application | Affects production speed and quality assurance |
| Testing Method | Methods like AOI, functional testing, and in-circuit testing | Ensures that PCBs function correctly and meet quality standards |
| Lead Time | Time taken from order to delivery of PCBs | Critical for timely product launches and commitments |
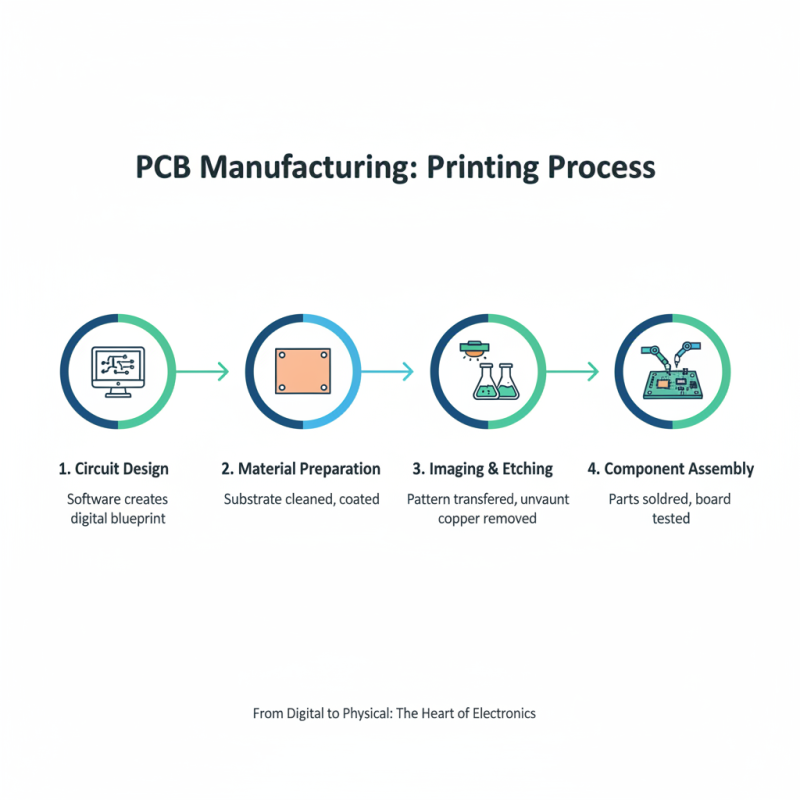
PCB printing is a crucial step in electronics manufacturing. The process begins with designing the circuit layout. Designers use specialized software to plan where every component will go. This digital blueprint is then translated into a physical board using various printing techniques.
One popular method is screen printing. It involves applying conductive ink onto the board through a mesh screen. This technique can be cost-effective, especially for larger production runs. However, it isn’t perfect. Fine details can sometimes get lost, requiring adjustments and revisions.
Another method is inkjet printing, which allows precision layer-by-layer application. This technique excels in intricate designs. Yet, it can face challenges with speed and consistency. It's essential to balance quality and efficiency in the printing process. Manufacturers often need to reflect on their choices and adapt to the evolving technology landscape.
PCB printing is a cornerstone of modern electronics manufacturing. It facilitates the creation of intricate circuits. These circuits are vital for the performance of electronic devices. By using advanced techniques, manufacturers can achieve high precision. This precision leads to enhanced reliability and functionality.
One major advantage of PCB printing is its ability to optimize space. Compact designs allow for smaller devices. Consumers often prefer slim gadgets that fit into pockets. However, it can be challenging to create reliable connections in tight spaces. Designers must balance size and performance carefully.
Moreover, PCB printing enhances thermal management. Effective heat dissipation is crucial for device longevity. Poor thermal design can lead to device failure. Engineers must address these challenges as they innovate. The process also promotes sustainability by minimizing waste. This is essential as the industry looks to reduce its environmental footprint. However, constant reflection on these practices is necessary.
Challenges in PCB printing present significant hurdles for manufacturers in modern electronics. One major issue is achieving precision in fine line printing. As products become smaller, the printed circuit boards (PCBs) must accommodate intricate designs. When the printing process is inaccurate, it leads to defects. These defects can ultimately result in product failure. The need for high-quality materials and advanced printing techniques is critical, but not always accessible for every manufacturer.
Another challenge arises from material compatibility. Not all inks bond well with various substrate materials. When mismatched, the longevity of the printed circuits can be compromised. Manufacturers may face the difficult task of selecting the right combination of ink and substrate. This requires ongoing research and development, which can be resource-intensive. Limited knowledge about advanced materials can lead to trial and error, delaying production times.
Lastly, the inspection process is often strenuous. Quality assurance is crucial, yet assessing every printed board for defects is tedious. Many manufacturers opt for automation, but setting up such systems can be costly. Some may lack sufficient training in this area. This uneven ground can result in gaps in quality control procedures. Continuous training and improvement are essential for meeting industry standards and ensuring reliability.
The evolution of PCB printing technology is shaping modern electronics. Emerging trends indicate a shift towards more efficient methods. The integration of automation is key.
Automated processes reduce human error and increase output. This change is beneficial, but it also requires skilled oversight.
3D printing is another exciting development. This technique allows for rapid prototyping. It accelerates the design process, but not without challenges. Material limitations can hinder growth. The need for reliable materials must be addressed.
This ensures long-lasting performance in electronic devices.
Sustainability is a growing concern in PCB manufacturing. Innovative approaches are being explored to minimize waste. Biodegradable materials offer promise, but their durability is often questioned. Balancing environmental impact with performance is essential. Continuous improvement is necessary for the future of PCB printing technology.